Revenue Recognition: Instalment Sales & Revenue from Contracts with Customers
(Quicknotes)
Related Terms:
Revenue- (PAS 18) gross inflow of economic
benefits during the period.
-arises in the course of the ordinary-including
sales, fees, interest, dividends, royalties, and rent
Gain- represent increases in economic benefit and such are no different in nature from revenue.
Ordinary Activities- core business operations
Gain- represent increases in economic benefit and such are no different in nature from revenue.
Ordinary Activities- core business operations
Revenue
is realized when goods and services are exchanged for cash or claims to cash
(receivables).
"Revenue is earned when the entity has substantially accomplished what it must do to be entitled to the benefits represented by the revenue."
Regular Sales- either cash sales or credit sales.
Installment Sales payment of periodic installment.
Method of Gross Profit Recognition
Time
of Sale/ Sale Basis (Accrual Basis)- profit is recognized in the period in
which the sale is made.
Time
of Collection- profit is recognized in the period in which cash is collected.
The gross profit is deferred, then it is realized when collections are made.
·
The installment sales method of accounting
normally implies the deferral gross profit but the recognition of selling and
administrative expenses in the period of their incurred.
· "The theory that costs and expense should be
matched against sales is applied in installment sales transactions through the
gross profit figure but no further."
· Allocation of Cost of Goods Sold
Use lump-sum is usually used for many cases.
· NRV= Estimated Selling Price-Recondition + cost
to sell)
·
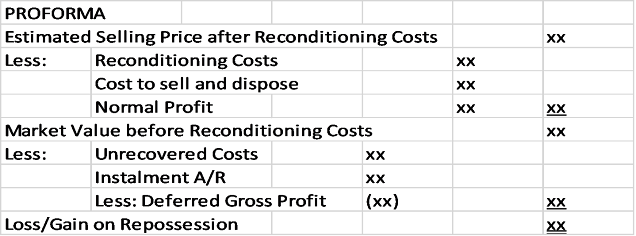
Guidelines in Repossession
1. Repossession may also be recorded as an estimated cash purchase.
2. When published prices are not available, NRV less normal profit may be used.
Journal Entry:
Repossessed
Merchandise xx
Deferred Gross
Profit
xx
Loss on Repossession xx
Installment Accounts
Receivable
xx
·
When a perpetual inventory system is maintained,
the account repossessed merchandise should be debited to Merchandise
Inventory-Repossessed
·
Trade-in- is recorded at the value allowed.
Over-allowance- a reduction in sales price
·
Uncollectible Allowance__Accounts Written-off
Doubtful Acct.
Expense xx
Deferred Gross Profit
XX
Installment A/R
xx
· Interest on Instalment Sales Contracts
a. Long-end interest- interest is computed based on
the balance of the unpaid principal balance between installment period
b. Short-end interest- interest is computed on the installment due, from the date the contract was entered into until the date of the installment payment.
·
Computation of Realized Gross Profit
Current Year Sales: Gross Profit/
Instalment Sales
Prior year’s Sales: Deferred-Gross
Profit-Beg. Of Current Year/Instalment A/R-beginning of the current year
·
No matter how it is displayed in financial
statements, deferred gross profit on installment sales is conceptually the valuation of an asset, that is, a reduction of assets.
·
The real estate acquired shall be considered as
the company’s inventory and are recorded in the same manner as a sale of
merchandise.
REVENUE FROM CONTRACTS WITH CUSTOMERS (IFRS 15)





.png)


0 Comments