CONFLICT IS EVERYWHERE
Source of Conflict
As business
defined management, it is an act of working with others to accomplish
tasks that fulfill its goals or objectives efficiently and effectively. During their management era, managers, at any level, experience
conflict which might be an obstacle in getting their desired results.
Conflicts are all over the place and are one of the major causes of business downfall suffered among major corporations, especially among the top managers, who have many disagreements with their subordinates (Argent). By proving that conflicts really exist, the clinical researcher presents a categorizing device for diagnosing the types of it. It is based on critical identifying characteristics and was clinically proven. They are namely- focusing on the conflict and the source of the conflict.
Conflict
focus is based on the substance of the dispute (what triggers the conflict)
that causes its escalation and is categorized into two: people-focused and
issue-focused. People-focused conflict is characterized by confrontations that
have a high effect level of emotional heat that is intensified or probably
triggered by moral indignation. Common situations are bitterness, false
accusation, and demand for justice; whereas issued-focus conflict is described
as an emotional dispute (more likely rational negotiation) and can be thought
of as a mutual decision between two or more people on how they allocate their
limited resources (Thompson).
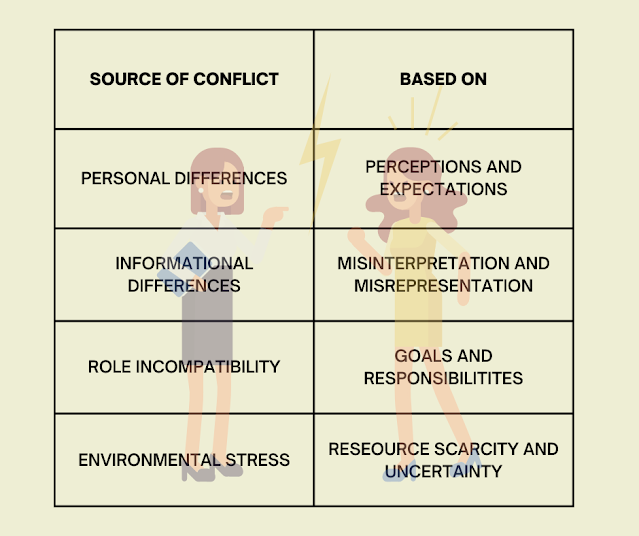
Another type of conflict is based on the source, they are personal differences, informational differences, role
incompatibility, and environmentally-induced stress. Personal differences
(perception and expectations) are common origins of conflict since every member
of an organization has different backgrounds since they have been molded by
society depending on their cultural and family differences that have a great
impact on their working environment. Simply stated, they are disagreements
about what is the correct thing to do based on facts against what is the
correct thing to do based on morals or norms, while, informational differences
are conflicts among members of an organization. It is characterized by
misinformation and misinterpretation.
Moreover,
role incompatibility is a mix between personal differences and informational
differences which affects the member’s responsibilities and organizational
goals. At the same time, environmental-induced stress is the primary source of conflict and
affects the resource scarcity and uncertainty of either members or the whole
organization itself. Uncertainty includes frequent and rapid changes in
accounting procedure, task assignments, management philosophy, and line of
authority.
Responding and Advantages of Conflicts
Any conflicting issues should be tackled with
management as soon as possible. There are five approaches in responding to
conflicts: a) The forcing response is an act to satisfy one’s own needs by
using their position or authority that makes the other party feels humiliated
or defeated, b) The accommodating approach is taking one side where one party
wins while the other will be neglected, c) The avoiding response is postponing
a solution or avoid to tackle the issue, d) compromising response is an act to
reach an agreement as quickly as possible to obtain a win-win situation for
both parties and e) collaborating approach is to solve the problem of both
parties.
Having a conflict can help the organization mature more. For most organizations, a moderate level of conflict is considered healthy because it is considered the lifeblood since it progresses and stimulates the vibrations of an organization (Brown). It enhances creativity, sparks innovation, and encourages the personal improvement of their staff. It helps the managers to become more diversified in terms of the demographic information of their subordinates and guides them on how to resolve more conflicts in the future (Blackard and Gibson). In fact, managers at any level, from different organizations and cultures, who deal with conflicts are a sign of organizational success considering the recent business trends toward globalization and joint ventures. Also, towards workforce diversification, managers who are flexible in resolving conflicts are an important indicator or predictor of organizational advancement (Seybolt, Derr and Nielson).
Works Cited
Argent, J. Corporate Collapse: The Causes and Symptoms. New York: Wiley, 1976.
Blackard, J and J Gibson. Capitalizing on Conflict: Strategies and Practices for Turning Conflict into Synergy in Organization: A Manager's Handbook. Palo Alto, CA: Davis-Black Publshing, 2002.
Brown, L.D. Managing Conflict at Organizational Interfaces. MA: Addison-Wesley, 1983. Reading.
Seybolt, P.M., C.B. Derr and T.R. Nielson. Linkages Between National Culture, Gender, and Conflict Management Style. University Utah, 1996. Working Paper.
Thompson, L. The Mind and Heart of the Negotiator, 2nd Ed. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall, 2001.





.png)

0 Comments